Medical Cannabis Treatment for Patients With Cataracts
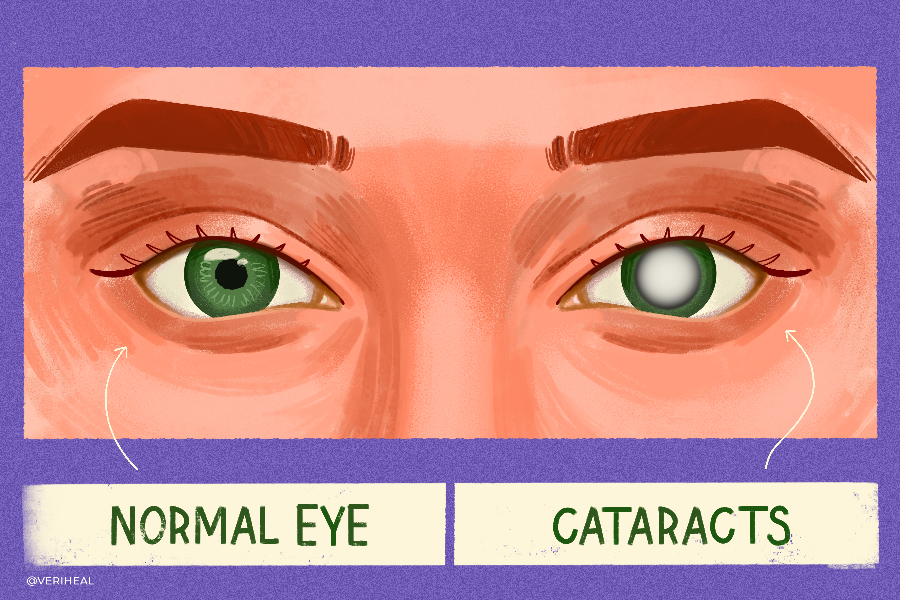
What You Need to Know: Medical Cannabis and Cataracts
While preliminary research hints at the potential benefits of cannabis for ocular health, particularly in relation to cataracts, the current scientific landscape lacks conclusive evidence. Cannabis, with its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, contains cannabinoids like cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) that may positively influence the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the eyes, which plays a role in regulating intraocular pressure.
More robust clinical trials are needed to firmly establish the efficacy and safety of cannabis for cataracts, but the intriguing connections between cannabinoids and ocular health are generating optimism among researchers. Patients interested in exploring alternative treatments for eye conditions, including the potential benefits of cannabis, are encouraged to engage in open discussions with eye care specialists. As scientific understanding evolves, cannabis may emerge as a promising avenue for supporting eye health, but it remains essential to approach the topic with a balanced perspective, considering individual health considerations, legal aspects, and the ongoing need for comprehensive scientific investigations.
The Science Behind Medical Cannabis for Cataracts
- How THC Might Help Patients With Cataracts
- The Symptoms of Cataracts
- Understanding the Different Types of Cataracts
- Cataracts and Cannabis Summary
Vision loss caused by eye diseases causes a considerable social and economic toll for millions of people including significant suffering, disability, loss of productivity, and diminished quality of life. According to national and state data, a majority of adult Americans do not seek eye care, and this is largely attributed to an aversion to the cost of care, lack of adequate health or eye insurance, or a failure to recognize warning signs (2).
Cataracts, cloudy spots in the eye lens, are expected to double by 2050, equaling up to 50 million Americans, according to the National Eye Institute (NEI) (3). Most cases of cataracts are among white men and women age 40 and over, with symptoms of the condition the same among all who suffer.
To date, there is no direct evidence that cannabis can help with cataracts. In fact, recent evidence shows smoking cannabis is linked to developing cataracts at a younger age, about 4-5 years earlier than expected. Cannabis smoke creates tar that contains some of the similar carcinogens of tobacco smoke, and so any kind of smoking should be avoided to prevent the development of cataracts. It may be possible that forms of cannabis ingestion other than smoking could be beneficial for other aspects of cataracts, but at this stage that is only generalized and direct research is still lacking (7).
How THC Might Help Patients With Cataracts
NEI reports surgery is the most common way to conquer cataracts. Other more natural ways to treat or prevent the condition include weight loss, stopping smoking, routine eye exams, managing comorbid conditions like hypertension and diabetes, adjusting lighting, and wearing UVB eye-protective, anti-glare sunglasses and prescription glasses or contacts. While there is no conclusive evidence that medical cannabis can adequately treat cataracts, it has proven to reduce inflammation and pain which are apparent in the condition and after surgery.
Medical Cannabis and Inflammation
When your body activates your immune system, it sends out inflammatory cells. These cells attack bacteria or heal damaged tissue. If your body sends out inflammatory cells when you are not sick or injured, you may have chronic inflammation. Inflammation is a symptom of many chronic diseases, such as arthritis or cataracts (5).
Inflammation is one of the most common conditions targeted with medical cannabis. Cannabinoids are known anti-inflammatory agents, more potent than Vitamin C or E (1). One of the most popular reports demonstrating that CBD is good for inflammation was published in a 2009 edition of Future Medicinal Chemistry.
“Cannabinoid receptors include CB1, which is predominantly expressed in the brain, and CB2, which is primarily found on the cells of the immune system,” according to the study. “The fact that both CB1 and CB2 receptors have been found on immune cells suggests that cannabinoids play an important role in the regulation of the immune system (9).”
Along with inflammation, high blood pressure is another cause of cataracts. High blood pressure is known to cause elevated eye pressures and inflammation which may result in cataracts. Studies show that medical cannabis has helped alleviate some side effects of pressure and pain in many parts of the body, including temporarily reducing eye pressure for 3-4 hours with THC. Pure CBD, on the other hand, can actually raise eye pressure.
High blood pressure is excluded as a section in this article because the research dedicated to the investigation of medical cannabis as a possible treatment for managing high blood pressure is still conflicting and in its infancy. Further research is needed to fully understand the impacts of cannabis on blood pressure.
Medical Cannabis and Pain Management
Cataracts are typically painless, but pain management can be an important part of managing post-surgical cataracts. Many physicians routinely use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Tylenol, or opioids for many cataract surgery cases.
Several studies have been performed showing that NSAIDs reduce inflammation, pain and general discomfort after cataract surgery (10). NSAIDs or other medications after cataract surgery are usually prescribed in high doses but for short periods of time.
However, long-term use of NSAIDs has a greater risk of potential side effects, especially for older people. Studies of older adults show that those with long-term chronic NSAID use increase their risk of:
- peptic ulcers
- renal failure
- stroke and heart disease
Chronic NSAID use also worsens many diseases, including heart disease and high blood pressure, which could exacerbate among people already experiencing hypertension in populations with cataracts. (4). Medical cannabis offers an alternative to NSAID use to manage pain post-surgery. Cannabis has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects that may help with pain management. It’s always advisable to consult with your doctor to establish the best treatment plan for your individual case.
While the AAO concedes that medical cannabis treats glaucoma, which has similar symptoms to cataracts, it is not feasible for long-term use due to the need for constant redosing and the impairing side effects that being high all the time carries.
“Research in the 1970s and 1980s did show a measurable decrease in intraocular pressure for three or four hours after smoking cannabis or ingesting THC as a pill or injection. But to treat glaucoma and save vision, eye pressure has to be controlled 24 hours a day,” reports the academy (12). Time will tell if medical cannabis can treat cataracts, especially with more private eye physicians prescribing it for patients who report seeing better with it.
The Symptoms of Cataracts
The rise of cataracts in the U.S. has steadily climbed. The NEI reports that between 2000 and 2010, cases rose by 20% in the decade from 20.5 million to 24.4 million, causing blurred vision in all who suffer, reports the NEI. The AAO reports the most significant symptoms of cataracts include seeing double, sensitivity to light, and only seeing faded colors. Other common signs and symptoms of cataracts may include:
- Clouded, blurred or dim vision
- Increasing difficulty with vision at night
- Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
- Seeing “halos” around lights
- Frequent changes in eyeglass or contact lens prescription (8)
While older age is the most significant cause of cataracts, other conditions can bring it on, genetics, diabetes, eye injury, ultraviolet ray damage, smoking and heavy alcohol use, and medications can also cause the vision condition. Some treatments for cataracts are riskier than others.
Cataract surgeries are very safe and are the recommended mainstay of cataract treatment with very few resulting in infection.Cannabis use is also not without side effects of its own and is not recommended for cataracts.
Understanding the Different Types of Cataracts
There are three main types of cataracts: nuclear sclerotic, cortical, and posterior subcapsular. However, there are about seven types of cataracts in total. To get a better understanding of these different classifications of cataracts let’s dive into some of the distinctions.
Nuclear Sclerotic Cataracts
This cataract is the most common and progresses slowly. Nuclear sclerotic cataracts originate in the central zone of the eye (called the nucleus) and begin with a gradual hardening and yellowing of the nucleus of the eye. This eventually spreads to other layers of the eye as it progresses.
A distinct characteristic of this type of cataract is that as it advances it creates what is known as second sight—a temporary improvement in near-sighted vision. However, as nuclear sclerotic cataracts develop further, vision ultimately declines.
Cortical Cataracts
Cortical cataracts have a different origin story than Nuclear Sclerotic cataracts. Where Nuclear Sclerotic cataracts start in the nucleus of the eye, cortical cataracts start from the outermost layer of the eye. As it develops it creates spokes that lead from the outside of the lens to the nucleus of the eye.
Some symptoms that are most commonly associated with cortical cataracts in particular are blurred vision, changes in contrast and depth perception, as well as difficulty with glare. It’s important to note that patients with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing cortical cataracts.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataracts
Posterior subcapsular cataracts develop quickly. Generally, this type of cataract progresses over a time span of months as opposed to years. Look out for changes in your night vision and increased difficulty reading for early warning signs.
Patients with diabetes or extreme nearsightedness are at an increased risk of this type of cataract. Additionally, those who use steroids are at a greater risk of developing posterior subcapsular cataracts.
Congenital Cataracts
Congenital cataracts are less common than age-related cataracts that develop in the elderly. However, when they do occur congenital cataracts are present at birth or form during early childhood. They are usually associated with genetics, other illnesses, radiation, steroid medications, infections during pregnancy, or trauma.
Secondary Cataracts
Secondary cataracts are most often caused by cataract surgery, and aren’t necessarily true cataracts. Up to half of cataract surgery patients will develop secondary cataracts months to years after the procedure. However, it can be easily fixed with specialized laser eye corrective surgery.
Secondary cataracts may also be caused by other diseases or medications. Diseases that are linked with the development of cataracts include glaucoma and diabetes. As mentioned previously, steroids can increase the likelihood of developing cataracts such as posterior subcapsular cataracts. Other medications can also cause the development of cataracts (14).
Traumatic Cataracts
Traumatic cataracts develop after an eye injury, but the effect is not immediate. In fact, it can take several years for traumatic cataracts to develop after the initial trauma.
Radiation Cataracts
Radiation cataracts, as the name suggests, can form after a person undergoes radiation treatment for cancer (3).
If you believe that you are developing cataracts it is important to visit your eye doctor or an ophthalmologist to seek eye care. Your eye doctor can help you assess treatment options that are best suited to your specific condition. Additionally, it is important to prioritize regular eye exams in order to maintain and improve your eye health over your lifetime.
Cataracts and Cannabis Summary
In summary, everyone needs routine eye exams and prompt specialist treatment for signs of cataracts. Diagnosis will require an eye exam including measurement of eye pressure. Cannabis cannot treat, prevent, mitigate, cure, or diagnose the development of cataracts.
Surgery will always be recommended as a permanent and safe fix for cataracts, and cannabis could potentially be useful for managing post-operative pain and pressure based on related data. However, there is no data yet to recommend cannabis for cataracts or post-surgical pain and your specialist may advise against it. Untreated and advanced cataracts can lead to blindness, so they should be taken seriously and treated timely and appropriately.
You should always discuss your healthcare options with your specialist provider and not defer safe, approved treatments like cataract surgery in favor of using cannabis on your own. Further studies are needed to prove any benefits or further detriments of cannabis for cataracts. At this point, smoking anything including cannabis appears to lead to an earlier onset of cataracts so this method should be avoided to prevent this and other health complications.
1. Atalay, S., Jarocka-Karpowicz, I., & Skrzydlewska, E. (2019). Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants, 9(1), 21. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/9/1/21
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, June 9). Fast facts of common eye disorders. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved March 29, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/visionhealth/basics/ced/fastfacts.htm#:~:text=Approximately%2012%20million%20people%2040,due%20to%20uncorrected%20refractive%20error
3. Delgado, A. (2017, September 29). Cataract: Types, causes and risk factors. Healthline. Retrieved March 29, 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/cataract#types
4. Hecht, M. (2019, July 23). NSAIDs and side effects: Common & Urgent. Healthline. Retrieved March 21, 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/side-effects-from-nsaids#long-term-side-effects
5. Inflammation: What is it, causes, symptoms & treatment. Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Retrieved March 21, 2022, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/21660-inflammation
6. Jadoon, K. A., Tan, G. D., & O’Sullivan, S. E. (2017). A single dose of cannabidiol reduces blood pressure in healthy volunteers in a randomized crossover study. JCI Insight, 2(12). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5470879/
7. Lehrer, S., & Rheinstein, P. H. (2022). Marijuana smoking and cataract. Journal Français D’Ophtalmologie, 45(3), 267–271. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35093261/
8. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2021, September 2). Cataracts. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved March 21, 2022, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cataracts/symptoms-causes/syc-20353790
9. Nagarkatti, P., Pandey, R., Rieder, S. A., Hegde, V. L., & Nagarkatti, M. (2009). Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Future Medicinal Chemistry, 1(7), 1333–1349. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828614/
10. Pain management in cataract and Refractive Surgery. Healio. (n.d.). Retrieved March 21, 2022, from https://www.healio.com/news/ophthalmology/20120331/pain-management-in-cataract-and-refractive-surgery
11. Russo, E. (2008). Cannabinoids in the management of difficult to treat pain. Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management, Volume 4, 245–259. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2503660/
12. Turbert, D., & Gudgel, D. (2021, March 8). Does marijuana help treat glaucoma or other eye conditions? American Academy of Ophthalmology. Retrieved March 21, 2022, from https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/medical-marijuana-glaucoma-treament
13. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.). Cataract data and Statistics. National Eye Institute. Retrieved March 21, 2022, from https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/outreach-campaigns-and-resources/eye-health-data-and-statistics/cataract-data-and-statistics
14. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.). Types of cataract. National Eye Institute. Retrieved March 31, 2022, from https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/cataracts/types-cataract