Does Marijuana Improve Artery Thickness from Arteriosclerosis?
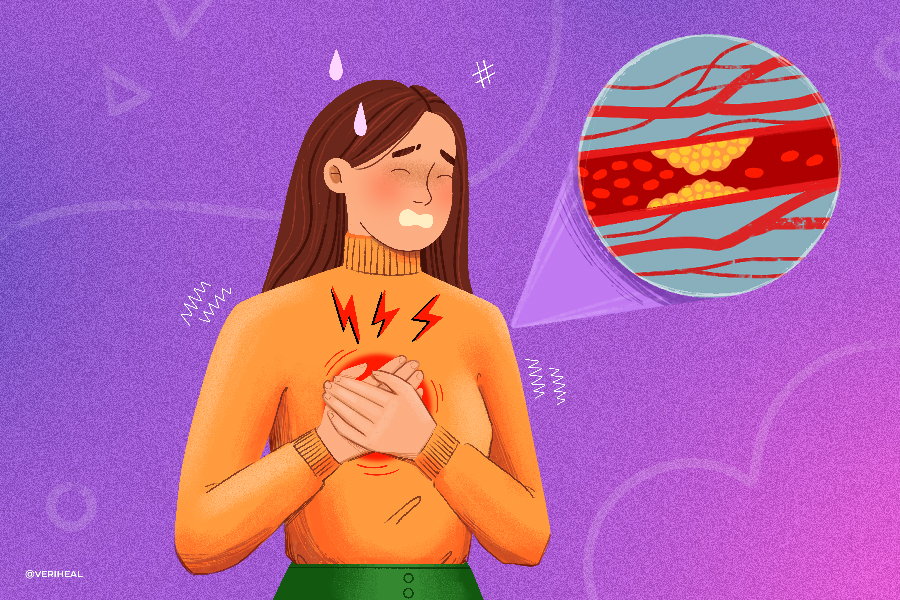
Arteriosclerosis is a group of conditions in which the arteries become stiff and hardened. This causes issues because arteries are responsible for carrying oxygen in the blood to the various organs and tissues of the body. Unfortunately, this can result in a lot of pain caused by circulation issues. Many of these patients are wondering if medical cannabis could help them feel better.
Medical cannabis contains natural chemical compounds called cannabinoids. This includes Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) which is known for the euphoria associated with cannabis and relaxing cannabidiol (CBD). When cannabis is inhaled or taken orally, these cannabinoids make contact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a system in the body that consists of endocannabinoids, or fat-based neurotransmitters, and a variety of receptors including cannabinoid receptors CB1 & CB2, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR), and other receptors.
When the receptors are activated by medical cannabis, the levels of endocannabinoids are increased or decreased. These endocannabinoids send out signals to other areas of the body which control a variety of processes including reducing inflammation and how we perceive pain. The ECS actions described here are part of a larger system in the body known as the endocannabinoidome (eCBome).
How Does the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) Play a Role in Atherosclerosis & Arteriosclerosis?
Medical cannabis has been shown to target inflammation in patients with atherosclerosis (27). Scientists believe that this is through cannabinoids contacting the CB1 & CB2 receptors in the endothelial cells that line arteries. This leads to changes in immune cells called cytokines and reduces monocyte immune cells being attracted to a protein called monocyte chemoattractant 1 (MCP-1). When Monocytes are slowed, the lesions inside the arteries that result from arteriosclerosis do not progress as rapidly.
Another method of the ECS helping with arteriosclerosis involves CBD and its ability to alter lipid peroxidation (12, 31, 27). This is a complicated process, but essentially lipids are fats in the body and include low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. LDL and HDL cholesterol are checked in metabolic blood tests.
Scientists have found that LDL cholesterol plays a role in the development of arteriosclerosis (27). This occurs through lipid peroxidation. Peroxidation is essentially damage to these fats caused by an imbalance of free radicals that are produced by cells in the body (20). Free radicals are unstable molecules that are produced by cells. They can build up in our cells, causing damage to our DNA, lipids, and proteins of the body.
CBD has been shown to act as an antioxidant and inhibit a specific free radical called 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX) in multiple studies (31, 26, 27). This free radical causes LDL cholesterol to oxidize, which causes damage and contributes to the formation of atherosclerosis.
Researchers believe that CBD may be able to decrease the progression of arteriosclerosis by preventing the formation of oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) cholesterol (27). CBD serves as a strong antioxidant in this case.
Are Cannabinoids an Option for Arteriosclerosis?
A 2005 study in mice serves as a pioneer for information regarding medical cannabis and arteriosclerosis. Using mice that were given 1 mg per kg a day, researchers were able to determine that cannabinoid receptor CB2 is a good target for treating arteriosclerosis. This is through downregulating immune cells that contribute to the inflammatory response in the body (28, 27). These immune system-modulating effects of cannabis have also been replicated in human samples (16).
A different study testing cannabinoid receptor antagonists found similar and beneficial results in mice receiving doses of rimonabant (25). Rimonabant is an anti-obesity drug and is known to interact with the endocannabinoid system (24). In addition to reducing the appetites of the mice in the study, rimonabant reduced blood cholesterol levels and the development of atherosclerosis lesions in the aorta of the heart (25).
Though this research did not specifically test medical cannabis and its cannabinoids, the results are exciting. This research shows that the pharmaceutical industry is utilizing cannabis-related research to improve arteriosclerosis and weight loss.
Can Cannabis Cause Arteriosclerosis?
Some research involving medical cannabis and arteriosclerosis shows that cannabis can increase the risk for this condition and other cardiovascular system conditions including heart failure, heart attack (myocardial infarction), arrhythmias, and changes in blood pressure.
Researchers think the cardiovascular risks of cannabis are due to a complex chain reaction that begins with THC or cannabis ingestion, CB1 receptor activation, and ends with decreased platelet-derived growth factors (PDGF). Decreased PDGF means that there may not be enough available for the smooth muscle cells that make up the heart and arteries (27).
Another reason why cannabis could potentially increase the risk of arteriosclerosis is by smoking it. Smoking tobacco, cannabis, or anything introduces more free radicals in the body. This increase leads to damage resulting in arteriosclerosis, cancer, and autoimmune diseases (13).
It is important to make informed decisions about any medications you put in your body, including the use of marijuana. Smoking anything, including cannabis is not recommended for patients with arteriosclerosis as well as lung or heart issues.
On the other hand, oral THC has also been shown to work as a temporary bronchodilator, which could help improve shortness of breath found in arteriosclerosis, COPD, and other lung disorders (15).
What Cannabis Preparations Are Suitable for Arteriosclerosis?
Medical cannabis should not be used to treat arteriosclerosis without approval from a qualified doctor, nor should it be used as a replacement for any FDA-legal medications you currently use. Since arteriosclerosis is often associated with shortness of breath, patients should avoid smoking or vaping cannabis to relieve their symptoms.
A range of alternative and discreet options are available, such as:
- Edibles
- Pills, capsules, and tablets
- Powder cannabis
- Cannabis flower
- Transdermal patches
- Tinctures
- Oral sprays
- Suppositories
What is Arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is a group of chronic inflammatory vascular diseases that targets the arteries (17). It is the underlying cause of around half of the deaths in Western culture (23). This arterial hardening and narrowing should not be confused with atherosclerosis, despite the two medical conditions often referred to as the same thing (4).
Atherosclerosis occurs when arteries, a type of blood vessel, thicken, harden and narrow due to plaque accumulation. This is caused by lesions that develop on the intima, or inner layer of arteries (17). Over time these lesions fill up with cellular waste that causes the walls of the artery to become thick and stiff.
Arteries transport oxygen and nutrients from the heart to the rest of the body. Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic, allowing the blood to circulate freely around the body. Plaques are considered a buildup of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in the body (4).
Plaques can block blood flow and can burst and lead to a blood clot or deprive various parts of the body of enough oxygen. When the arteries harden it is simply called hardening of the arteries (4).
Arteriosclerosis is considered a type of cardiovascular disease and can lead to other serious issues including (17):
- Aortic aneurysms
- Coronary artery disease (CAD)
- Carotid artery disease
- Peripheral artery disease
Symptoms of having arteriosclerosis or one of these more severe conditions may include (17):
- Squeezing pain and pressure in the chest, arms, and shoulders
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Vision problems
- Sudden and severe headaches
- Numbness or weakness in the limbs or face
- Loss of balance
- Leg pain
- Poor wound healing
- Back pain
- Chronic pain
- Blood in the urine
- High blood pressure
- Kidney complications or failure
Types of Arteriosclerosis
There are three different types of arteriosclerosis that are discussed below. These are distinct conditions, but can easily be mixed up as the names are similar.
Arteriolosclerosis
Arteriolosclerosis is very similar to arteriosclerosis. It occurs in smaller arteries and arterioles which are tiny blood vessels that branch off into capillaries (17). Patients are at a higher risk for arteriosclerosis if they have uncontrolled diabetes, hypertension, or use certain medications. This is because these conditions can cause damage to the smaller blood vessels of the body.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis affects the elastic and large arteries in which there is atheroma formation. The progressive disease occurs when cholesterol, fats, and other substances block blood flow inside the artery. In serious cases of atherosclerosis, plaque buildup can explode, leading to a blood clot and heart attack or stroke (4).
Doctors may refer to atherosclerosis as a heart problem, but it can impact all types of arteries (4). It is preventable with healthy lifestyle habits. Doctors may prescribe cholesterol medications and anticoagulants for symptomatic relief. Symptoms sometimes go unnoticed until the arterial blockages become so extreme that they can’t supply adequate blood to vital organs and tissues.
Having high cholesterol or obesity increases the risk of atherosclerosis. Other risk factors include tobacco smoking, high blood pressure, and diabetes (17).
Möenckeberg Medial Calcific Sclerosis
This rare type of arteriosclerosis occurs as a result of calcium buildup in the artery wall’s middle layer (tunica media) (17). When this layer becomes calcified, the artery walls start to stiffen.
People over the age of 50 are at higher risk, as are those with underlying medical conditions. Cardiovascular conditions are a complication of Möenckeberg medial calcific sclerosis (7).
Talking to Your Doctor About Arteriosclerosis Diagnosis & Treatments
The most important way to prevent arteriosclerosis is to visit your healthcare provider routinely or as recommended to manage your conditions that increase the risk of arteriosclerosis in the first place.
If you are at risk for or think you have signs of arteriosclerosis, arrange a meeting with your chosen healthcare provider for a screening. The sooner you manage your chronic conditions (e.g. diabetes, high blood pressure, smoking, etc.) for prevention or once you are diagnosed, the sooner you can get medical treatment to prevent the problem from progressing into a heart attack, stroke, or another serious medical emergency.
Your doctor can screen for preliminary signs of arteriosclerosis during a visit, such as asking about or looking for chest pain (angina), drooping facial muscles, leg pain, numbness, foot exams, and lack of blood flow.
They will ask about your medical history, and use a stethoscope to measure blood pressure and listen to your arteries for signs of restricted blood flow, e.g. a “bruit” – an audible vascular sound that indicates a blood flow obstacle.
Depending on the risk factors presented during your initial doctor’s appointment, some further tests may be required, including:
- Ankle-brachial Index (ABI): Blood pressure in the ankle and upper arm (brachium) can be compared using a non-invasive ABI test. A ratio below 0.9 may indicate peripheral artery disease (PAD) (3).
- Cardiac imaging tests: Your doctor will use a CT scan, MRI, PET, X-ray, and doppler ultrasound scans to check heart and vessel health.
- Cerebral angiography: This minimally invasive test enables your doctor to analyze blood circulation through the blood vessels.
- Coronary calcium scan: This is a CT test that identifies calcium deposits in the coronary arteries and calculates your risk of developing heart disease.
- Heart function tests: These tests involve the use of an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram to assess heart strength and functioning.
- Stress tests: Heart rhythm, blood pressure, and breathing are monitored during a stress test. This type of exercise test typically involves the use of a stationary bike or treadmill (30).
Complementary Treatments Worth Discussing with Your Doctor
Examples of complementary medicine that are generally welcomed in cases of arteriosclerosis include stress relief techniques, such as meditation, and the consumption of nutritional supplements like calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
B vitamins may assist the body in breaking down homocysteine – an amino acid that has been associated with an increased risk of heart problems (9). You can also reduce the risk of developing arteriosclerosis with preventative care, such as by engaging in regular exercise, following a healthy diet, and quitting smoking.
While medical marijuana and other complementary medicines can prove beneficial for you or a loved one with arteriosclerosis, it’s important that you continue visiting your doctor routinely and using any medications that are prescribed by your doctor.
Note: Veriheal does not intend to give this as professional medical advice. Do not attempt to self-diagnose, or prescribe treatment based on the information provided on this page. Always consult a physician before making any decision on the treatment of a medical condition.
1. Abstract 643: Type-2 Cannabinoid Receptor Deficiency is Associated with Atherosclerotic Lesion Calcification in Ldlr-null Mice | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/atvb.36.suppl_1.643
2. Activated Endocannabinoid System in Coronary Artery Disease and Antiinflammatory Effects of Cannabinoid 1 Receptor Blockade on Macrophages | Circulation. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.811992
3. Ankle Brachial Index Test. (2021, April 28). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ankle-brachial-index-test
4. Arteriosclerosis / atherosclerosis—Symptoms and causes. (n.d.). Mayo Clinic. Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/arteriosclerosis-atherosclerosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20350569
5. Arteriosclerosis: Definitions | American Journal of Clinical Pathology | Oxford Academic. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://academic.oup.com/ajcp/article-abstract/24/4/472/1767850?redirectedFrom=fulltext&login=false
6. Arteriosclerosis Types. (2009, November 23). News-Medical.Net. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Arteriosclerosis-Types.aspx
7. Arteriosclerosis: What You Need to Know About Hardening of the Arteries. (n.d.). Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24870-arteriosclerosis
8. Arteriosclerosis—Symptoms and Causes. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/arteriosclerosis
9. Atherosclerosis | Complementary and Alternative Medicine | St. Luke’s Hospital. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.stlukes-stl.com/health-content/medicine/33/000016.htm
10. Atherosclerosis – What Is Atherosclerosis? | NHLBI, NIH. (2022, March 24). https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/atherosclerosis
11. Atherosclerosis Vs. Arteriosclerosis: What’s The Difference? (2022, October 5). Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/atherosclerosis-vs-arteriosclerosis
12. Chan, J. Z., & Duncan, R. E. (2021). Regulatory Effects of Cannabidiol on Mitochondrial Functions: A Review. Cells, 10(5), 1251. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051251
13. Definition of free radical—NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms—NCI (nciglobal,ncienterprise). (2011, February 2). [NciAppModulePage]. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/free-radical
14. Delta 9-Tetrahydrocannabinol regulates Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in activated human T cells—PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12446015/
15. Gong, H., Tashkin, D. P., Simmons, M. S., Calvarese, B., & Shapiro, B. J. (1984). Acute and subacute bronchial effects of oral cannabinoids. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 35(1), 26–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/clpt.1984.4
16. Han, K. H., Lim, S., Ryu, J., Lee, C.-W., Kim, Y., Kang, J.-H., Kang, S.-S., Ahn, Y. K., Park, C.-S., & Kim, J. J. (2009). CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors differentially regulate the production of reactive oxygen species by macrophages. Cardiovascular Research, 84(3), 378–386. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvp240
17. What You Need to Know About Arteriosclerosis. Verywell Health. Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/arteriosclerosis-overview-and-more-5087299
18. Jett, J., Stone, E., Warren, G., & Cummings, K. M. (2018). Cannabis Use, Lung Cancer, and Related Issues. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 13(4), 480–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2017.12.013
19. Jiang, L., Pu, J., Han, Z., Hu, L., & He, B. (2009). Role of activated endocannabinoid system in regulation of cellular cholesterol metabolism in macrophages. Cardiovascular Research, 81(4), 805–813. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvn344
20. Lipid Peroxidation: Production, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal—PMC. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4066722/
21. Marijuana linked to heart disease; supplement may mitigate risk, study reports | News Center | Stanford Medicine. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://med.stanford.edu/news/all-news/2022/04/marijuana-heart-disease.html
22. Nagarkatti, P., Pandey, R., Rieder, S. A., Hegde, V. L., & Nagarkatti, M. (2009). Cannabinoids as novel anti-inflammatory drugs. Future Medicinal Chemistry, 1(7), 1333–1349. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.09.93
23. Pahwa, R., & Jialal, I. (2023). Atherosclerosis. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507799/
24. Rimonabant. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB06155
25. Rimonabant, a Selective Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonist, Inhibits Atherosclerosis in LDL Receptor–Deficient Mice | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.168757
26. Role of Oxidative Modifications in Atherosclerosis | Physiological Reviews. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/physrev.00047.2003?rfr_dat=cr_pub++0pubmed&url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org
27. Singla, S., Sachdeva, R., & Mehta, J. L. (2012). Cannabinoids and Atherosclerotic Coronary Heart Disease. Clinical Cardiology, 35(6), 329–335. https://doi.org/10.1002/clc.21962
28. Steffens, S., Veillard, N. R., Arnaud, C., Pelli, G., Burger, F., Staub, C., Karsak, M., Zimmer, A., Frossard, J.-L., & Mach, F. (2005). Low dose oral cannabinoid therapy reduces progression of atherosclerosis in mice. Nature, 434(7034), 782–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03389
29. Stocker, R., & Keaney, J. F. (2004). Role of oxidative modifications in atherosclerosis. Physiological Reviews, 84(4), 1381–1478. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00047.2003
30. Stress test—Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Retrieved April 27, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/stress-test/about/pac-20385234
31. Takeda, S., Usami, N., Yamamoto, I., & Watanabe, K. (2009). Cannabidiol-2′,6′-Dimethyl Ether, a Cannabidiol Derivative, Is a Highly Potent and Selective 15-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 37(8), 1733–1737. https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.109.026930